AIoT: The Intersection of AI and IoT in Smart City Evolution
By Mr. Sudhir Kunder, CBO of DE-CIX India
The Power of AIoT in Smart Cities
Cities are undergoing a profound transformation through the convergence of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), known as AIoT. This integration is revolutionising urban landscapes, making them more intelligent, efficient, and responsive to citizens’ needs. With AI adoption in India growing by 60% in the past three years and IoT penetration expected to reach 80% by 2025, AIoT is poised to redefine urban living (Source: NASSCOM, IDC).
Transforming Urban Living with AIoT
Smarter Traffic Management
Traffic congestion remains a major challenge for urban infrastructure. AIoT-driven solutions leverage real-time data from traffic sensors, connected vehicles, and surveillance cameras to analyse traffic patterns and dynamically adjust signals. Cities like Singapore & Moscow have reported a 20% reduction in congestion with AI-based adaptive traffic lights (Source: World Economic Forum). Similar implementations in India’s metro cities could significantly enhance traffic flow and public transport efficiency.
Predictive Infrastructure Maintenance
Aging infrastructure demands proactive upkeep. AIoT sensors embedded in roads, bridges, and water pipelines detect wear-and-tear while AI predicts failures before they occur. This predictive maintenance model reduces costs by up to 30% and extends infrastructure life by 20% (Source: McKinsey & Company). Cities like Tokyo and Barcelona have successfully deployed AI-powered monitoring to prevent large-scale disruptions.
Smart Energy Management
Energy efficiency is key to sustainable urbanisation. AIoT-powered smart grids analyse real-time consumption, optimise distribution, and integrate renewable sources. By predicting peak usage, AIoT ensures efficient energy management. In India, over 50% of major power grids are deploying AI-driven solutions, supported by government-backed smart grid projects (Source: Ministry of Power, India).
Advanced Public Safety and Surveillance
AI-powered surveillance, integrated with IoT-enabled cameras and sensors, enhances urban security. Facial recognition and predictive analytics aid authorities in preventing crimes before they occur. China’s AI surveillance networks have led to a 30% decline in crime rates in monitored regions (Source: MIT Technology Review). In India, AI-driven public safety solutions are expected to scale with the expansion of 5G networks by Reliance Jio and Airtel.
Disaster Response & Environmental Monitoring
AIoT plays a crucial role in early disaster detection and environmental monitoring. Real-time data on air quality, weather conditions, and seismic activity helps authorities issue timely warnings and deploy emergency responses. AI-driven flood prediction models in the Netherlands have improved evacuation planning by 40%, setting a precedent for India’s flood-prone regions (Source: European Commission on Disaster Risk Reduction).
Challenges & Ethical Considerations
Despite its advantages, AIoT adoption faces hurdles like data privacy concerns, cybersecurity risks, and high deployment costs. With India drafting the Personal Data Protection Bill, it is crucial to strike a balance between innovation and responsible AIoT implementation.
Recent AI and IoT Developments in India
AI and IoT in Urban Infrastructure
India’s rapid urbanisation necessitates sustainable and efficient infrastructure. AI and IoT technologies are pivotal in realising the country’s ‘Viksit Bharat 2047’ vision for development. Government-backed smart city initiatives are driving digital transformation at scale.
Technological Showcases in Smart Cities
The Convergence India & Smart Cities India Expo 2025, themed ‘Imagining an AI-Driven Future Today,’ highlights India’s strides in AI and IoT. With over 1,00,000 participants, the expo showcases innovations that position India as a global leader in digital urban solutions.
AI in Public Safety at Mass Gatherings
The 2025 Maha Kumbh Mela in Prayagraj, dubbed the “Digital Maha Kumbh”, is set to use AI-driven facial recognition and crowd monitoring technologies. With an expected 400 million visitors over six weeks, AIoT solutions will enhance public safety, monitor crowd density, and prevent stampedes (Source: Uttar Pradesh Government Digital Initiative).
The Role of DE-CIX India in Enabling AIoT-Powered Smart Cities
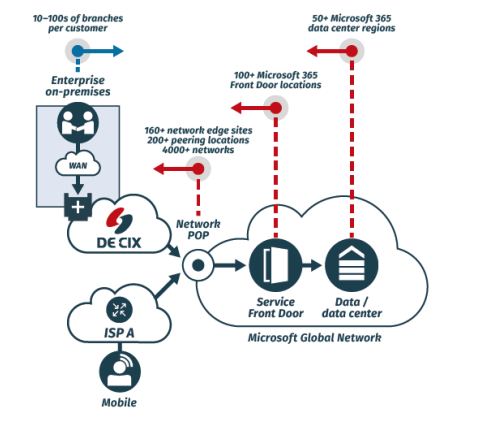
As India’s leading Internet Exchange, DE-CIX India plays a vital role in AIoT integration by ensuring ultra-low latency, high-speed, and secure data exchange. AIoT applications depend on real-time data processing—from traffic management to predictive infrastructure maintenance—and DE-CIX India facilitates seamless interconnectivity. By strengthening digital infrastructure, DE-CIX accelerates smart city innovation and supports India’s transition to an interconnected urban ecosystem.
The Future of AIoT in Smart Cities
The adoption of AIoT is no longer a matter of ‘if’ but ‘how fast.’ Cities investing in AIoT-driven transformation will be better equipped to address challenges in urbanisation, sustainability, and resource optimisation. Collaboration between governments, enterprises, and technology leaders will be key to realising AIoT’s full potential in shaping the cities of tomorrow.
About Mr. Sudhir Kunder, CBO of DE-CIX India
Mr. Sudhir Kunder, Chief Business Officer at DE-CIX India, brings over 30+ years of expertise in telecommunications, FMCG, retail, and ICT. Specialising in Corporate Governance, Strategic Planning, and Service Management, he plays a pivotal role in shaping DE-CIX India’s vision. A strong advocate of situational leadership, he fosters collaboration, innovation, and strategic growth.
About DE-CIX India
DE-CIX India is a premier Interconnection Platform, facilitating seamless peering between major Indian and global networks. With presence in Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, DE-CIX enhances internet performance for ISPs, CDNs, OTT platforms, and enterprises, strengthening India’s digital economy.