BGP Basics
BGP Basics
A router receives prefix announcements through eBGP, with your network either being multi-homed or peering to receive announcements for the same prefix from multiple sources. Among these, the router selects the optimal prefix announcement, which is then utilized for routing decisions.
The following criteria helps in the selection of the best prefix announcement:
- Each prefix needs (wants) only one single path
- Always the same decision, with the same parameters, making it deterministic
- Based on the attributes of the BGP announcement
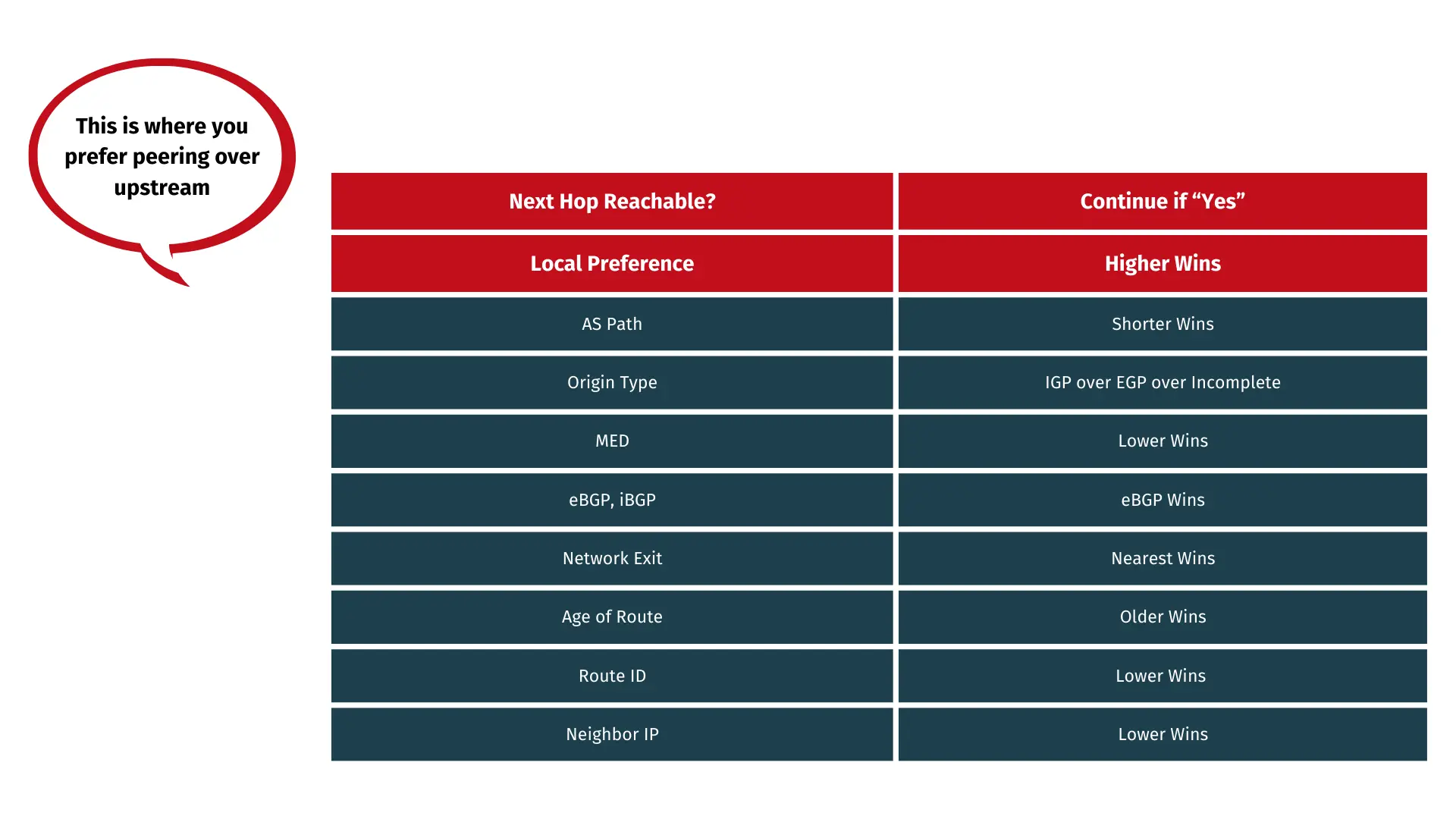
The following example, based on the BGP routing algorithm as outlined in RFC 4271, illustrates how your network selects the appropriate prefix for routing decisions:
- Your router will check if next hop is reachable
- Your router chooses the route with the highest local preference
- Your router prefers the route with shortest AS path
- Your router prefers the route with the lowest origin attribute
- Your router prefers the route with the lowest MED Value
- Your router prefers the routes received from eBGP
- Your router prefers the routes learned from the router with lower router ID
- Your router prefers the routes learned from the router with lower IP address
- In terms of your internal routing protocol, your router prefers the nearest exit from the network
- Dependent on implementation : prefers more stable,(= older) routes
*Important rules are in bold while implementations are more vendor-specific
The router determines the next hop only after selecting the best path. The DE-CIX Academy Knowledge Card on BGP Routing is provided below. You can also download it here

